[[{“value”:”
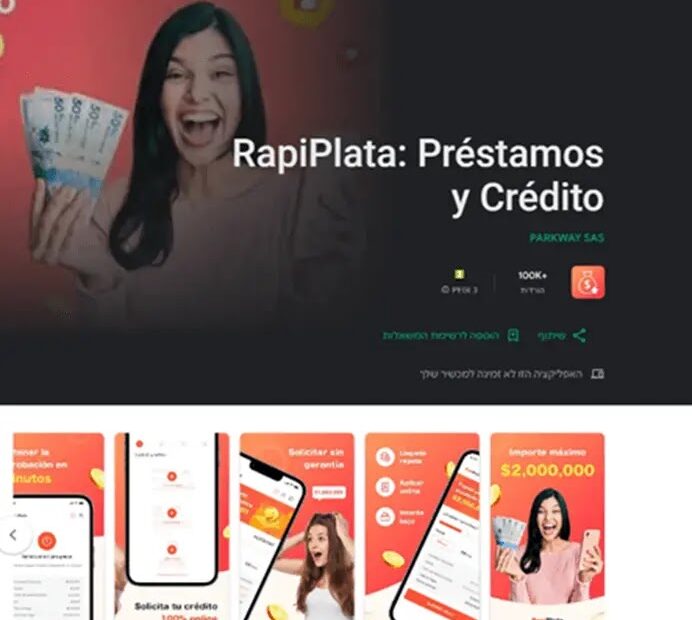
A malicious loan application masquerading as a legitimate financial service has infected over 150,000 iOS and Android devices before being removed from official app stores.
The app, identified as “RapiPlata,” achieved a Top 20 ranking in the finance category on SimilarWeb’s platform in Colombia, demonstrating the widespread impact of this sophisticated threat.
.webp)
While approximately 100,000 victims downloaded the application from Google Play, the remainder obtained it through the Apple App Store, highlighting vulnerabilities in both platforms’ security screening processes.
.webp)
The fraudulent application presented itself as a quick loan service targeting Colombian users but concealed extensive data theft capabilities behind its seemingly legitimate interface.
Once installed, RapiPlata requested permissions far beyond what would be necessary for loan processing, including access to SMS messages, call logs, calendar events, and lists of installed applications.
The app claimed these permissions were needed for creditworthiness assessment and payment reminders, but in reality, they enabled comprehensive surveillance of users’ devices.
Check Point researchers identified the malicious application in February 2025 through their Harmony Mobile detection engines, which flagged the app as malicious using advanced machine learning models.
Their analysis revealed that RapiPlata is part of a larger SpyLoan malware operation with connections to previously identified threats. Most concerning was the minimal detection coverage on VirusTotal, allowing the malware to operate undetected for months before removal.
Victims reported severe consequences beyond mere data theft, including harassment through messages and emails.
The attackers frequently threatened users with being labeled as delinquent debtors despite many never having received any actual loans.
In some cases, the app operators contacted victims’ contacts from stolen address books, falsely claiming outstanding debts and damaging personal reputations.
These social engineering tactics compounded the technical exploitation, creating both digital and real-world consequences for affected users.
Despite its removal from official stores in March 2025, RapiPlata continues to pose threats through alternative distribution channels.
The application’s website remains operational and deceptively displays a Google Play download button that redirects users to external sites for unauthorized app installation.
.webp)
This redirect chain (using URLs like https[:]//t[.]copii[.]co/9YEPe) demonstrates the operators’ determination to maintain their malicious campaign despite increased scrutiny.
The app’s most sophisticated feature was its comprehensive data exfiltration mechanism. Upon first launch, RapiPlata scanned all SMS messages for specific keywords, ostensibly to evaluate financial standing.
However, the keyword list revealed broader surveillance intentions, including mundane Spanish terms like “día” (day), “hasta” (until), “para” (for), and “sido” (been) that have minimal financial relevance.
This extensive scanning effectively captured nearly all communications, which were then uploaded to command-and-control servers for analysis and exploitation.
Calendar exfiltration proved particularly dangerous for corporate users, as it often contained Zoom meeting links and presentation attachments.
Attackers could leverage this intelligence to join sensitive corporate discussions undetected, accessing intellectual property and strategic business information.
Similarly, call logs enabled mapping of social and professional relationships, facilitating targeted spear-phishing campaigns against contacts in the victim’s network.
Automate threat response with ANY.RUN’s TI Feeds—Enrich alerts and block malicious IPs across all endpoints -> Request full access
The post Malicious Loan App on iOS & Google Play Store Infected 150K+ Users Devices appeared first on Cyber Security News.
“}]]
Read More .webp) Cyber Security News
Cyber Security News